Do you know that the rain cycle is a continuous process of water circulation between the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere? This complete process exerts a profound influence on agriculture. Rainfall plays a critical role in providing water for crops. The reasons being it replenishes the soil moisture and supports irrigation practices.
The timing and duration of rainfall are crucial factors. It is what actually determines crop growth and development, as different crops have specific water needs at different stages.

Moreover, the rain cycle impacts groundwater availability, soil erosion, and nutrient-leaching. The occurrence of pests and diseases is also affected by it. Therefore, understanding the intricate relationship between the rain cycle and agriculture is crucial for sustainable farming practices. In the long run, it ensures food security as well.
Rain Cycles – Their Impact on Agriculture
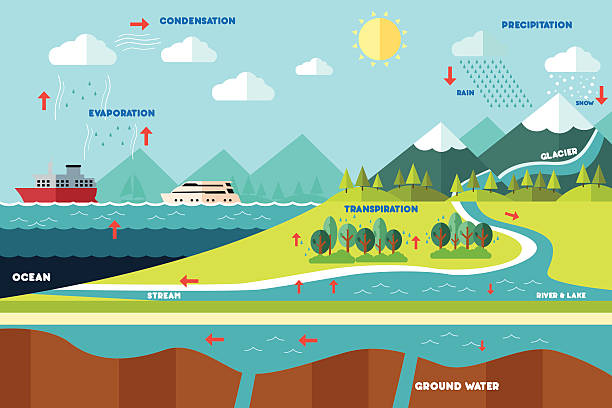
The rain cycle, the water cycle, or the hydrological cycle plays a crucial role in agriculture. It is a continuous process through which water is circulated between the atmosphere and the Earth. This cycle is driven by solar energy and involves several stages. It includes evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff. The availability and timing of rainfall significantly impact agricultural practices. As a result, it also affects crop productivity.
Rain provides water to the crops
Firstly, rain is essential for providing water to crops. Evaporation from oceans, lakes, and rivers forms clouds in the atmosphere. When these moisture-laden clouds reach a saturation point, precipitation occurs in the form of rain.
Adequate rainfall is crucial for crop growth as it replenishes soil moisture and provides water for irrigation. Insufficient or irregular rain can lead to drought, which can be disastrous for agriculture. Drought conditions can cause water stress in crops, resulting in stunted growth, reduced yields, and even crop failure.

Moreover, the timing and duration of rainfall are critical factors for agricultural success. Different crops have specific water requirements at various stages of growth. For example, crops require frequent and light rainfall during the germination and early growth stages. Whereas during the reproductive phase, they need a relatively drier period. If rainfall patterns do not align with these requirements, crop development and yield can be negatively affected.
The rain cycle also influences the availability and quality of groundwater. It is a vital water source for irrigation in many agricultural regions. Adequate rainfall replenishes groundwater reserves. It ensures a sustainable supply of water for crops. On the other hand, extended dry periods with minimal rainfall can deplete groundwater reserves. In the long run, it can lead to water scarcity and increased competition for water resources.
Rainfall pattern affecting agriculture
Rainfall patterns and intensity can also impact soil erosion and nutrient leaching. Heavy rainfall events can cause soil erosion, washing away topsoil and valuable nutrients. This can degrade soil fertility and reduce agricultural productivity over time.

On the other hand, light and steady rainfall help the soil absorb water more efficiently, allowing plants to access essential nutrients dissolved in the water. Balanced rainfall patterns help maintain soil structure and promote healthy root development.
Rainf cycle affecting pests and diseases
In addition to its direct impact on crops, the rain cycle influences the occurrence of pests and diseases. Excessive rainfall and humidity create favorable conditions for pests, fungi, and bacteria growth. These pests can damage crops and reduce yields.
On the other hand, prolonged dry periods can accumulate pests and diseases due to weakened crop resilience. Hence it is crucial to understand that a well-distributed rainfall pattern will help maintain a balanced ecosystem. At the same time, it can also reduce the risk of pest outbreaks.
Rain Cycle – An Integral Part of Water Storage
Water storage in the rain cycle is one of the most crucial aspects. Water is stored in three main places – the atmosphere, Earth’s surface, and underground. It encompasses various reservoirs such as oceans, glaciers, groundwater, lakes, soil moisture, the atmosphere, and rivers. Collectively, all these water storage areas make up the hydrosphere. Do you know that more than 97 percent of the world’s water in the oceans is salt water?

As you know, the majority of water is in the oceans. It is seen as the starting and ending point of the cycle. Water that starts from the sea evaporates up into the atmosphere. But in the end, most of it falls back into the ocean as rain. Additionally, a much smaller amount falls onto land as rainfall.

Water movement between reservoirs occurs through diverse transport mechanisms, with each pool having its own residence time. Soil moisture lasts a few months. Atmospheric water is renewed every few weeks. Do you know that great lakes replenish every few decades, and groundwater can last centuries? Interestingly, ice caps retain water for thousands of years. The nature of geological features, soil types, and underground rocks plays a significant role. All these factors help to determine the storage characteristics on land and underground.
Conclusion
Thus, the rain cycle is vital for agricultural productivity and sustainability. Adequate and well-distributed rainfall provides water for irrigation. At the same time, it replenishes groundwater reserves, supports nutrient uptake by plants, and helps maintain soil fertility.
In contrast, irregular rainfall patterns, droughts, or excessive rainfall can have detrimental effects on crops. It could lead to reduced yields, water stress, and soil erosion. All this can lead to increased pest and disease pressure.
Understanding the dynamics of the rain cycle and its impact on agriculture is essential for effective water management. With sufficient knowledge, crop planning and mitigating the risks associated with climate variability are also possible.
Read related topics on soil texture, seeds and plants, manual irrigation, plant nursery in Dubai, plant nursery, water sprinkler, green leaf manure, cruciferous vegetables, types of organic farming, sprinkler system, pest control UAE, outdoor plants UAE, pest control services, and vegetable farm. You can also read about ground water, sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, types of farming, tropical fruits, and more.





Leave a Reply